Common Eye Conditions
Facts about Diabetic Retinopathy
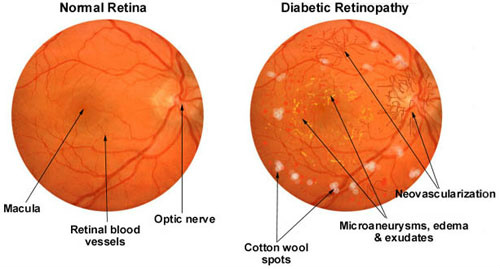
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is an eye condition where the retina is damaged due to diabetes mellitus (DM). If left untreated it can lead to extensive vision loss or even blindness. It is due to damage of the blood vessels in the eye which is caused by high blood sugar levels.
Individuals with Type 1 diabetes are more at risk if there is poor glucose control.
What are the Symptoms?
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy and other diabetes-related eye problems include:
- Sudden myopia (short sightedness)
- Cataracts
- Eye pain
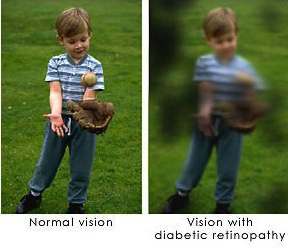
- Double, fluctuating, blurry or distorted vision
- Eye floaters and/or blind spots (in the late stages of diabetic retinopathy)
- Corneal defects or corneal wounds that are slow to heal
- Scotoma (shadow in the eyes’ view field)
- Presbyopia-unrelated near vision issues
Other signs that an Ophthalmologists/ Optometrist may find during an eye exam including swelling of the retina, traces of blood deposits or fluid leakages from blood vessels.They then may refer for further tests if they deem it necessary.
If diagnosed with diabetes, see an Optometrist or an Ophthalmologist once a year for a dilated eye examination. It is also recommended to have your eyes evaluated shortly after a diabetic diagnosis is made.
Diabetic Eye Diseases
Who Are at Risk?
- Diabetics unable to control blood sugar levels are most at risk of diabetic retinopathy.
- Smoking
- Uncontrolled Hypertension may aggravate diabetes leading to potential retinopathy
- Women who develop diabetes during pregnancy are also at higher risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- African-Americans have double the risk of going blind due to diabetic complications, particularly at a young age. Other minorities are also at higher risk including Hispanics and Latino.
- Anyone with a family history of diabetes; either type 1 or type 2 are also at risk of themselves developing diabetes. Often if type 2 diabetes develops, it is firstly detected during a routine eye exam. This is why it is important for regular dilated eye examinations for anyone who may be at risk.
Diabetic Retinopathy Prevention
With regular check-ups and proper treatment, diabetic retinopathy is a condition that can be prevented or curtailed. By controlling blood sugar levels and attending all regular check ups, the possibility of diabetic retinopathy can be reduced.
In order to ensure this:
- Regularly monitor blood sugar and keep it well under control within the normal limits
- Maintain a healthy diet; smoking and alcohol are best avoided
- Practice regular exercise.
- Follow your doctor’s advice, attending all your regular check-up s including a yearly dilated eye examination
Diabetics in Ireland who have poor vision may be able to register with the National Council for the Blind in Ireland (NCBI) which permits them to avail of certain services and statutory benefits.